By Chris Pearson, President, 5G Americas
It sometimes seems one of the hardest things to realize is when you are living through an historical revolution. Like steam power, electricity, gas, oil, electronics, computers and telecommunications before it, the first three Industrial Revolutions are making way for our current Fourth Industrial Revolution: the blurring of lines between physical, digital, and biological spheres.
“Difficulty is the excuse history never accepts.” – Edward R. Murrow
The anchor technologies of Industry 4.0 include artificial intelligence / machine learning, autonomous vehicles, cloud and edge computing, robotics, virtual and augmented reality, drones, precision medicine, and of course – 5G. It is the collision and intertwining of these technologies that will shape and re-shape the modern world in ways we can’t yet even imagine. 5G could be in the middle of it all.
Let’s face it, the modern world is mobile. However, it’s extremely resource-prohibitive to run wires everywhere you want. Yet consumer demand for data continues to drive new innovations as new applications, services and intelligence continue to be pushed further from the data center to the network edge and through the air interface to all types of devices. While previous generations of wireless cellular have been good at delivering “best effort” connectivity, the new age is calling for the addition of very specialized types of data based on the specific needs of the customer’s service or application.
The fifth generation of wireless cellular, or “5G”, is extremely powerful in delivering on core three use cases: enhanced mobile broadband with peak theoretical data throughput up to 20 Gbps (up from 1 Gbps for 4G LTE); ultra-reliable low latency as low as one millisecond (down from 10 msec for 4G LTE) and six nines of reliability; as well as massive device management of up to one million devices per square kilometer.
These capabilities of 5G networks map broadly into key categories of IoT:
- Broadband IoT to provide large volumes of data transfer
- Critical IoT uses that need ultra-high reliability and low latency
- Industrial Automation IoT that integrate 5G into Ethernet-based industrial protocols
- Massive IoT for low-cost sensors and devices with small data volumes and extreme coverage
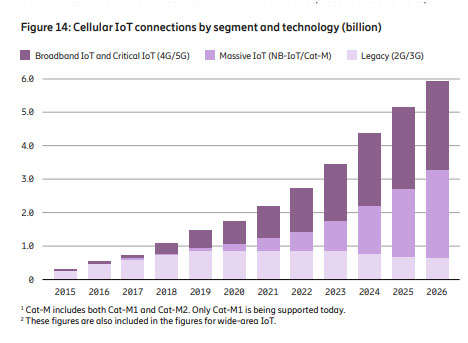
Of these four different types of IoT use cases, wireless cellular offers several options, including both 4G LTE and 5G networks for many Broadband and Critical IoT applications, as well as Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) and Cat-M for Massive IoT cases. According to Ericsson, NB-IoT and Cat-M based on the 4G LTE standard will account for 45 percent of all cellular IoT connections by 2026. In the Industrial Automation IoT category, 5G fixed wireless access, private networks and network slicing offer excellent opportunities to complement or augment enterprise Ethernet capabilities.
Source: Ericsson Mobility Report, November 2020
One aspect of 5G separates it from all previous generations of wireless cellular before it is time-critical communications that will offer new opportunities in a variety of industries. The ability to precisely time data flows to an unprecedented degree will be a bedrock capability for delivering real-time media for teleconferencing and VR/AR, remote control for drones and machinery, industrial control for automated supply chains, as well as mobility automation.
The ability to drive time-critical communications have broad applications across additional uses, such as cloud-assisted basic AR, remote control with haptic feedback in industrial settings, automated container transport in ports, or even machine vision for robotics. The possibilities are nearly endless, reaching across industries as diverse as entertainment, automotive, public safety, forestry, or health care.
In fact,Markets & Marketsresearch projects just the global 5G IoT market size alone is expected to grow from USD $0.7 billion in 2020 to USD $6.3 billion by 2025. Manufacturing, specifically, is the fastest growing enterprise market for 5Gwith an expected CAGR of 134% between 2020-2028, according to Research and Markets, which will be fueled by an estimated 75+ billion installed IoT devices by 2025, creating up to USD $2.7 trillion in economic impact for factories.
Companies are now making major changes to their businesses, processes, supply chains, and partner ecosystems to ensure they land on the right side of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. It is important for entities not to be hesitant in embracing new technology opportunities in this quickly changing environment as digital, physical, and biological spheres begin to collide.
For a deeper dive on how 5G and IoT will intersect, check out our5G Americas white paper, 5G: The Future of IoT, where we take a look into the 5G IoT market, examine more use cases such as smart grids, smart homes, and connected cars, as well as outline theIoT requirements that are being addressed in 3GPP Release 16 and 17 global standards, changes in 5G network architecture and 5G IoT solutions that will help to shape the future of the industry.
About 5G Americas: The Voice of 5G and LTE for the Americas
5G Americas is an industry trade organization composed of leading telecommunications service providers and manufacturers. The organization’s mission is to facilitate and advocate for the advancement and transformation of LTE, 5G and beyond throughout the Americas. 5G Americas is invested in developing a connected wireless community while leading 5G development for all the Americas. 5G Americas is headquartered in Bellevue, Washington. More information is available at 5G Americas website and Twitter.
5G Americas’ Board of Governors Members include AT&T, Cable & Wireless, Ciena, Cisco, CommScope, Crown Castle, Ericsson, Intel, Mavenir, Nokia, Qualcomm Incorporated, Samsung, Shaw Communications Inc., T-Mobile US, Inc., Telefónica, VMware and WOM.
About Chris Pearson
 By Chris Pearson, President, 5G Americas
By Chris Pearson, President, 5G Americas
Chris Pearson is the President of 5G Americas. In his executive role, he is responsible for the overall planning of the organization and providing management for the integration of strategy and operations in the areas of technology, marketing, public relations and regulatory affairs.












