A key element of Industry 4.0 implementations, Edge Computing and 5G are providing the next generation of private wireless networks for our connected world enabling digital transformation.
In order to leverage the power of AI, machine learning and automation deployments for the industry, mines, utilities and smart cities, they will need highly reliable and secure wireless connectivity and edge computing infrastructure. Private wireless provides a single network for voice, video and data i.e business-critical OT applications. It supports low-latency 5G device to device communications, low-power IoT sensor connectivity, mission-critical voice and video radio communications and legacy serial communications for SCADA and other control systems. Current private/enterprise connectivity including CAT cabling and IT- based wireless systems, such as Wi-Fi, cannot meet these requirements on their own. These systems will need to be supplemented or fully replaced by private wireless based on 5G. Radio access points provide coverage for outdoor and indoor spaces, similar to Wi-Fi, but with fewer endpoints. Unlike Wi-Fi, there is a core network, which is the key to the mobility aspect, security and maintaining quality-of-service parameters. Depending on the size of the premise, dedicated 5G core can run on a dedicated Edge computing with 2-3 physical servers deployed in a server room or inside a smart rack in an industrial setup.
Private 5GaaS
Cutting-edge manufacturing sites, distribution centers and numerous other campus environments can benefit from the deployment of a private 5G infrastructure supporting various spectrums of 5G radio access networks. From algorithmic updates to a production processes, predictive maintenance of machinery and real-time interaction with autonomous distribution vehicles, private 5G networks offers numerous advantages for modern enterprises. The Private 5G Software Stack delivers value from intelligent 5G Private Network ecosystem running on distributed private edge cloud consists of:
- IP Backhaul – IP/MPLS Routing and Forwarding Software containing OSPF, ISIS, BGP, LDP, PIM. The routing software can be integrated to a COTS appliance to route the private 5G traffic between 5G Radio to the Edge Applications
- 5G Core – 5G core software for Mobility, Authentication, Security, Session and Policy Management. It contains of the AMF, SMF and UPF 5G Functions. The 5G core software is hosted on COTS server as VNF or CNF.
SDN Controller – Provides centralized management, orchestration, zero touch provisioning, network provisioning and monitoring of network nodes.
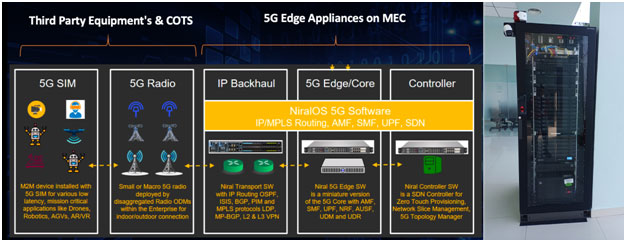
While aiming to democratize private 5G as a service, Edge, and Cloud networking infrastructure via embracing a vendor-agnostic, open-source, web-scale, and disaggregated approach, leveraging 5GC – Network Operating System (NOS) integrated to ORAN 5G RU running on the Smart Edge. Its fully managed with scalability and flexibility as a key enabler for digital transformation. A hub-and-spoke topology enables centralized management and control of the distributed Edge environment, as illustrated in Figure 2. The spokes are compute-enabled edge nodes hosted by a global network of data center partners, enabling SpeedCloud Edge to deploy workloads geographically. This approach delivers high performance and low latency wherever it is needed, while also offering regionalized services and meeting local standards and regulatory requirements. Centralized orchestration provisions and manages edge nodes and automates the deployment and lifecycles of containerized workloads.

USE CASES
Figure 2 : Hub-and-Spoke Topology
Smart edge simplifies the deployment and management of container- based applications and workloads at the network edge. The platform provides a distributed, centrally managed Kubernetes infrastructure, unified storage and integrated network services such as routing, switching and firewalling. Together, these components form the smart distributed cloud computing platform. The solution abstracts away the complexity of provisioning and maintaining cloud infrastructure, so IT organizations can increase their effectiveness by focusing on more value-added activities.
5G is the next big thing with a complete software-defined architecture that includes cloud based network function virtualization and automation, Industry 4.0 applications will reap the benefits of true multivendor networks that are harmonized with a common feature set across all target markets / workloads, with this the mobile network infrastructure deployment changes drastically at the fundamental level. Since 5G is completely software defined stack, operated on the shared spectrum industries can leverage private 5G
running on the edge replacing their WIFI Network and leverage faster speeds and lower latencies of 5G new radio, NR n78 operating band developed by 3GPP, often using unlicensed or shared spectrum called CBRS, particularly helpful for private M2M communication for Industrial Automation IoT used for robotics, video surveillance, drones and smart devices / sensors used within the smart factory premise.
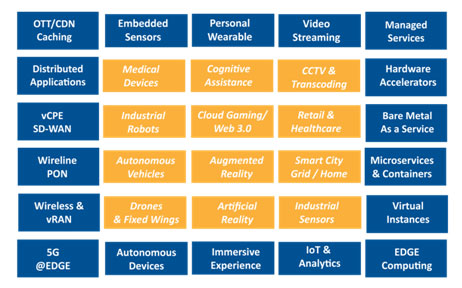
Private 5G opportunities in India
India had 1.2 billion mobile subscribers in 2021, of which about 750 million were smartphone users according to Deloitte’s 2022 Global TMT (Technology, Media and Entertainment, Telecom) predicts India will have one billion smartphone users by 2026 with rural areas driving the sale of Internet-enabled phones. The prediction will drive consumption and generate massive demand for localization of data at a much lower latency. India is witnessing a transition from an emerging to a developed market economy and digital is slated to play a key role in this journey. Digital is not only catalysing economic growth across all sectors and sub-sectors, but also forms the bedrock for providing better services to citizens, enabling social and financial inclusion, enhancing productivity and helping create a connected ecosystem. The size of the digital economy in India is estimated to grow from $ 200 billion in 2017-18 to a staggering $ 1 trillion by 2025 as mentioned in the Meity draft data center policy 2020.
India has around 375 MW installed power capacity for Data Centre and as per projections, this may grow to three time by 2025, and the Meity intends to accelerate the projected Data Centre growth and investments in the sector via driving necessary regulatory, structural and procedural interventions for enabling ease of doing business in this sector. As we have illustrated above that the data center ecosystem is also gearing up for distributed computing and enablement of industrial things ( Read, IIoT) it is prudent to deliberate on few opportunities for Edge computing usecases in India across key sectors such as healthcare, education, manufacturing, social wellbeing / smart cities and fintech.
Healthcare – Smart Hospitals powered by Edge
Over the last few years, healthcare strategists focus on clinical decision support (CDS), helping provide clinicians with timely, filtered, and patient-specific information they can use to enhance care, this pursuit has seen a growing number of medical devices introduced to healthcare environments. These range from embedded devices in medical equipment’s, tablets and wearables to health monitors and artificial intelligence (AI)-powered imaging systems. Smart devices give clinicians a timely status of key patient vitals
such as heart rate and blood pressure, internal body imagery and aid remote care by collecting patient data and triggering actions based remediations.
On the other hand, AI-powered imaging models can detect potential concerns in X-rays, MRI’s prioritizing those images for radiologist or physician review, there are many such examples that demand collection, processing, analytics and storage of large amount of data and algorithms. Edge computing brings data processing, analytics, and storage closer to the source as on-premise edge at a hospital, speciality clinic or a mobile edge device at a patient’s home. Edge computing works as a complement to the cloud, help us choose where to best place workloads along the compute spectrum. With over 11000 govt hospitals across India, edge computing can become vital enabler for critical applications such as NIC’s eHospital with OPD, IPD, Lab/LIS, Radiology/RIS and Billing modules further bridging the gap of better HealthCare across India and social wellbeing of all Indian citizens. Similar usecases on the private hospitals that can leverage the distributed edge computing techniques to further their digital spectrum of patient and administration services.
Education – EdTech is the new Edge
As part of a learnt lesson, the pandemic has adversely impacted the education sector, mostly in the rural areas, the EdTech sector is now on the radar with special focus of policy makers for the content creation, collaboration and consumption across India. We all witnessed the potential of virtual classrooms and online learning, Edge computing allows students and teachers to quickly and seamlessly interact in virtual classrooms and improves virtual experiences and learning outcomes without dependency on external network and cloud connectivity.
With on premise syndication of the classroom content between multiple edge locations transforms the content delivery, on demand learning and digital media management that can foster effective collaboration of content across multiple languages and syllabuses. Using applications running on the edge leveraging AR/VR, Video transcoding and analytics students and faculty can leverage interactive learning experience as they prioritize connectivity and networking across several campuses and remote faculties. India has over 45,000 degree colleges, over 1000 universities and has over 14 lac schools run by govt and private educational trusts, most these are partially enabled with digital eco system and offer great opportunity landscape for Edge computing, for sure.
Manufacturing – Smart Factories leverage Edge
Industrial automation is the name of the game today, modern manufacturing is merging Information technology (IT) with operational technology (OT) for predictive analytics, automating controls and monitoring processes, improving production efficiency, energy management and optimizing logistics via emerging technologies such as AI/ML, IIoT and Data Science. All of these emerging technologies demand an infrastructure that can manage the massive amounts of data ingestion, processing endpoint devices that send and receive machine to machine communication and cannot afford network latencies to move the data and controlled instructions between shop floor robotics to remote cloud and vice versa. This becomes perfect use case for Smart Edge Deployment.
Ingesting, analyzing, and acting on factory floor data in real time, as part for Industry 4.0 charter many smart factories are witnessing billions of data points generated through modern applications and integrated smart / CNC machines, advanced sensor technologies, AR/VR simulated environments, 3D modelling, CAD data, and AI-enhanced machining processes etc using big data for analytics on edge. Edge computing is now offering them profound benefits for reducing downtime / machine malfunctions, predictive maintenance, and thus improving quality, higher yields, reduced wastage, increased throughput, and lower overall costs.
As per CEIC, India Manufacturing Industries data reported 242,395,000+ number of Factories/manufacturing locations in India with 16 key clusters hosting Petroleum, refinery, petrochemicals, pharmaceutical, chemicals, cement, sugar, Steel and ancillary industries, fertiliser, metal fabrication, paper, shipbuilding, jewellery, leather, textiles, Automobile and automotive parts, Seafood, fisheries, Agri products, FMCGs etc. the yearly growth rate of 2-3% since 2018-19, industry accounted for about 14.5 percent of the country’s GVA in fiscal year 2021.
Smart Surveillance – Smart City Applications on Edge
Around 1.54 million public facing cameras are spread among India’s top 15 cities. New Delhi (5,51,500), Hyderabad (3,75,000), Chennai (2,80,000), and Indore (2,00,600) have the most surveillance cameras in the country, this coverage can provide lot of opportunities if the feeds are ingested, transcoded and processed with AI/ML based algorithms at the Edge. Today these feeds are not effectively corelated to find a person or vehicle across all running cameras/feeds instantaneously, the low latency applications that are used for facial recognition, advanced surveillance can leverage edge computing for automated monitoring and result in much better value addition than the manual monitoring of feeds in the silos. All feeds before analytics should be transcoded for required bitrate, codec to ensure interoperability between applications and storage, the processing at edge helps manage the feeds and run the video analytics on the edge for near real time results. Edge locations can store the feeds for active monitoring as well as push the feeds to cloud storage for long term archival required for regulatory purposes. Feeds from public places, airports, bus / train stations could provide much more insights of count of people / vehicles using the premises, crowd control and route / capacity planning of public transportation etc.
For smart cities edge deployments could support applications for smart bins, solid waste management, public transportation, citizen centric applications and data analytics use cases, it would also be important for effective monitoring and control of traffic, disaster management and surveillance of sensitive areas and assets across the city feeding the intelligence back to central command center. The edge deployments across key locations will also reduce the dependency on the core datacenter and provide redundancy to applications, datasets and digital services as well.
Fintech – Banking and Digital payment
As we transverse the banking landscape, payment related frauds, identification and authorization, eKYC and rural banking are few areas that can get benefits from edge computing at the branches. Since edge computing delivers low latency analytics that guarantees data sovereignty and security fostering the cybersecurity, data loss / fraud prevention via real-time geo-location tagging, digital footprint analyzer, suspicious beneficiary detection, micro expression analysis, AI/ML based eKYC, Biometric authentication via facial expressions etc applications that can be hosted on the edge offloading the non-core banking applications at the edge. With advanced surveillance running at the edge, banks can do effective workforce balance and productivity analysis wrt customer footfall at the branches and can leverage edge data processing and can help these businesses distribute data more quickly by minimizing data delays from remote cloud servers thus boosting revenue.
Conclusion
Using distributed edge computing, organizations can streamline the deployment of applications and workloads to the network edge using a robust, cloud-native model based on open source software components and optimized for augmenting modern commodity hardware and infrastructure seamlessly. Placing compute and storage at the edge reduces costs associated with wide-area network bandwidth consumption and enables latency-sensitive usages based on highly distributed data sources. Many Edge applications can take advantage of running private 5G on Edge that benefits, including performance, control, reliability, and density for demanding enterprise workloads such as Industry 4.0, as well as future 5G network
slicing capabilities for improved quality of service and lesser hassles of rerouting, upgrading and manageability of wired networks on the shop floor. Container infrastructure hosted on distributed 5G Edge helps streamline network transformation, adding global scale on-demand to edge computing environments. smart 5G edge can also be a key enabler for container-as-a-service (CaaS), which lets development teams deploy containerized software without concerning themselves with lower-level infrastructural details and provides convergence of voice, video and data centric applications as a unified deployment model. These models and others offer a robust on-ramp for businesses to profit from the symbiotic relationship between cloud computing and processing at the edge. The future of datacenter is clearly cloud based distributed computing leveraging private 5G, for sure!












