By textbook definition, Customer Journey refers to the set of interactions that a customer has with a brand during their engagement with its service. In retail, customer journey is a depiction of all the stages customers go through when interacting with the retail brand, from buying products to accessing customer service to airing grievances on social media. A Customer Journey Map is a pictorial representation of the same which helps in understanding the holistic story of customers’ experiences with the brand across all touchpoints.
Consider a customer who is looking to purchase a new television, either through a physical store or through online. The very first step is to search for the television either through the web or physically going into stores. He/she may be presented with choices on type (LED vs OLED), brand, size (55 vs 65), etc. and based on his/her preferences (and budget) he/she narrows down on a single model. This phase of narrowing down on the product is called Pre-Purchase.
Once he/she has made his choice, he/she adds the television to the Cart (either physical cart or digital) and proceeds towards checkout, sometimes purchasing other related items, say a pair of speakers and an HDMI cable along the way. This second phase, from product selection to checkout, is called Purchase.
The third and final phase, called Post-Purchase, is about continuing the engagement of the customer and the brand after the purchase has happened, such as registration of the television, servicing, troubleshooting, returns/replacements in case of defects and other after-sales services.
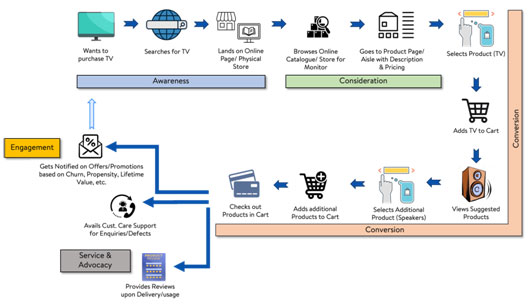
Throughout this customer journey, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) plays a huge role in ensuring a hassle-free customer shopping journey, along with creating avenues for revenue growth of the brand. In Pre-Purchase, the main themes are awareness and consideration, which deals with how to make the customers aware of the product and guide them towards locating the product. In Purchase, the focus is on conversion, i.e. how to convert a visit into a purchase, and gradually increase basket size and frequency of purchase. Post-Purchase is all about service & advocacy, ensuring a seamless after-sales service and understanding customers’ sentiments/grievances, and also about re-engagement, to ensure that customers keep on engaging with the brand in future.
The below sections describe in detail, how AI and ML are involved in each of the three phases.
Pre-Purchase. As mentioned before, in order to purchase a product the customer first needs awareness on where (which store/ecommerce platform) the product is available. Marketing through advertisements is the primary way of achieving the same, and ML Models such as Market Mix Modeling, Multi-touch Attributions are widely used in ad spending optimization to ensure the correct ads are reaching the correct person. Further customization on which ads to show to which customers are performed by building customer segments using Clustering Algorithms like DBSCAN, SOM on various customer facets such as demographics, age, gender, census information among others. Also, if a retail channel has both store and online options, look-alike models can help in identifying store/online only customers so that they can be converted into omni customers (shopping both in online and retail).Speaking of online, there also exists a vast majority of people who browse through items without purchasing anything; and clustering algorithms on clickstream data can help identify these segments. Once these segments are identified, Acquisition Models are used to customize advertisements and even provide personalized campaigns/promotions for each of these segments.
For online purchases, automated Shopper Guide Bots harness the power of AI to navigate a customer towards purchase in case they are facing any technical difficulties. Other areas where AI plays a role include Natural Language Processing (NLP) Models to enhance user search experience (Voice/Image Search, Auto Complete), augmented reality to recreate a physical store virtually; and Compliance Models to ensure correct/compliant product information display.
Purchase. The Purchase Phase involves guiding the customer to purchase the product and also parallelly attempting to add more products to his/her Cart while he/she makes the purchase. In such scenarios, Recommendation Engines are heavily used to identify related products the Customer might be interested in. For online, these come up as products in “Items you may want to purchase” section. For stores, there is an additional Machine Learning Layer wherein Assortment Optimization is used to ensure items purchased together are placed together and/or bundled as part of promotions, so as to attract the customer’s attention. These frequently bought items are identified through Machine Learning Algorithms like Apriori and FPGrowth. In ecommerce, Propensity Modelling is used for auto-filling baskets which work on behalf of a shopper to fill specific needs like regular purchase of common products. Other Techniques like out-of-stock substitution, shop-the-look are also used to ensure an overall increase in the Customers Basket size. Newer AI areas to ensure seamless checkouts include Cashierless stores withs elf-checkout options.
Post-Purchase. Natural Language Processing based solutions are widely used during post-purchase, where Chat and Voice-Enabled Bots are used to understand customer intent and reply via AI suggested responses. To handle the scale, Cognitive Computing is utilized to auto-respond to many customer service inquiries up to a certain level before actual human representatives have to take over. Sentiment Analysis Modules like BERT, HMMs are also used to extract sentiments from customer feedback to understand and improve product quality and service.
Retention and re-engaging these customers (into making more purchases) is vital to the health of the brand, and here customers are grouped into various buckets in order to target them in a customized manner. This itself in a mammoth task and needs an article on its own, but in brief, below are some ML techniques used to bucket customers:
- Loyalty Modeling to segregate loyal customers
- Customer Lifetime Value Models to distinguish high, medium and low-value customers
- Customer Churn Model to pinpoint customers who are at risk of leaving
- Uplift Model to target customers who are likely to respond to promotions
In conclusion, AI and ML play a pivotal role in mapping a customer journey, even before they have made a purchase. Customer journey maps provide a way of stepping into the customers’ shoes and observe the service from their perspective. However, one must understand that it is by no means a silver bullet, and there are many misconceptions about the purpose of customer journey mapping and maps. But when you know what you’re doing and doing it for the right reasons, customer journey mapping undoubtedly can have a very positive impact on the business and customers. With AI and ML guiding the way, these maps help in prioritizing activities that make an actual impact on customers and business which in turn improve internal collaboration and alignment.












